We used almost all existing electrophysiological techniques to register cell activities both in cultures and brain slices, for instance:
-whole-cell and cell-attached patch-clamp recordings
-perforated patch recordings
-extracellular recordings
Digital imaging:
This approach allows measuring of different intracellular ion concentrations, including sodium, calcium, potassium. Using voltage-sensitive dyes one can record membrane potentials.
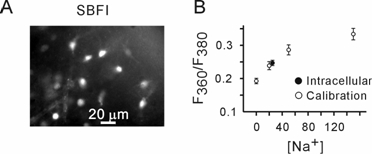
This image shows a staining of astrocytes in the neocortical brain slices with a Na+-sensitive indicator (SBFI). Because SBFI is a ratiometric probe, it is possible to perform quantitative measurements of intracellular sodium concentrations.
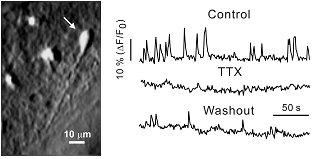
In this case, a neocortical cell was loaded with a calcium dye Oregon-1 and action potentials were recorded as calcium transients.Tetrodotoxin (TTX), an antagonist of voltage-dependent Na+ channels, eliminated the observed activity.
Histology and Immunohistochemistry:
After an experiment cells can be further characterized using different intracellular fillings (e.g. Biocytin) or antibody stainings and confocal microscopy.
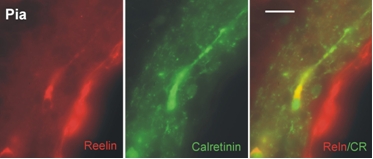
Images show stainings of neocortical neuron (Cajal-Retzius cell) with anti-Reelin and anti-Calretinin anibodies.